怎樣使用XML實(shí)現(xiàn)多渠道接入網(wǎng)站的構(gòu)架_Xml教程
推薦:解讀從實(shí)際應(yīng)用中了解WML學(xué)習(xí)自然語(yǔ)言的最好方法就是溶入相應(yīng)的語(yǔ)言環(huán)境在交流中學(xué)習(xí),學(xué)習(xí)一種編程語(yǔ)言的最好方法就是看例程。為了幫助大家建立wml應(yīng)用的第一印象,所以請(qǐng)大家先看第一個(gè)例子:
一.背景
在現(xiàn)在的網(wǎng)站中,接入的渠道是越來(lái)越多了,技術(shù)也是越來(lái)越先進(jìn),WAP, SMS,EMAIL, 傳統(tǒng)的Web, Socket等等,如果連數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)和LDAP也算接入的話,那在設(shè)計(jì)之中需要擴(kuò)展的空間要做到很好 很好,才保證在添加新的渠道情況下不需要更多的修改代碼甚至不改代碼的情況。但可能嗎?我想也不可能,但有什么方式可以更好的解決這種多渠道接入的框架的完美性呢?
二.構(gòu)架
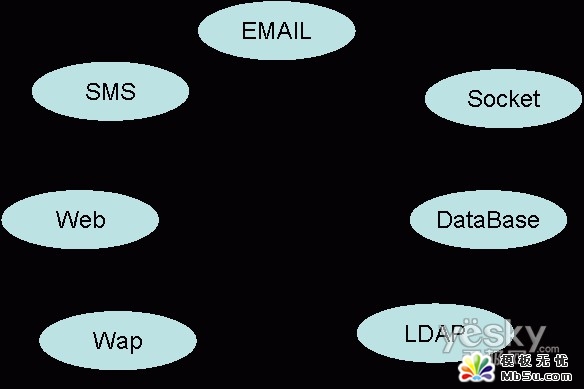
【圖一】
如圖一所顯示,在現(xiàn)有的所有接入都已經(jīng)使用上的時(shí)候,設(shè)計(jì)者看的都眼花繚亂了,如果是為了湊份子,那這些程序怎么寫(xiě)都可以,而且也肯定可以實(shí)現(xiàn),但維護(hù)起來(lái)就會(huì)比較痛苦,還是回到那個(gè)問(wèn)題,怎么可以實(shí)現(xiàn)更完美呢?如圖二顯示:
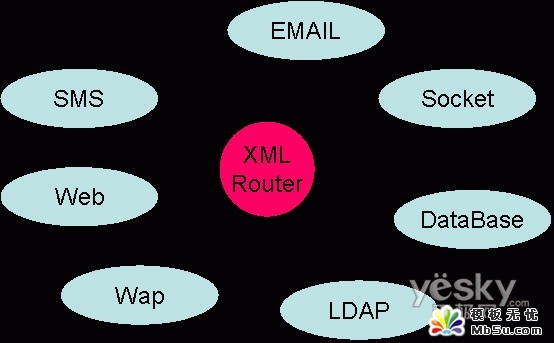
【圖二】
圖二看起來(lái)象個(gè)八爪的章魚(yú),章魚(yú)腿分別連接所有的接入渠道,進(jìn)行連接所有這些渠道的核心就是這個(gè)章魚(yú)的頭XMLRouter,Router在此的作用是溝通所有渠道,實(shí)現(xiàn)數(shù)據(jù)的路由,爭(zhēng)強(qiáng)系統(tǒng)在構(gòu)架上的擴(kuò)展性和靈活性,好處會(huì)很多很多。稱呼為XMLRouter是因?yàn)槿绻皇褂肵ML這種靈活而又規(guī)范的語(yǔ)言來(lái)做為數(shù)據(jù)傳輸?shù)拿浇?那Router的工作量也同樣會(huì)成倍的增加,定義好XML的規(guī)范后將為以后的擴(kuò)展帶來(lái)很多好處。
三.思想和模式
XMLRouter的最初想法來(lái)自于計(jì)算機(jī)的主板和<
Services思想:為了能和Router進(jìn)行溝通,在這些渠道接入時(shí)必須定義統(tǒng)一的接口,這里成為Services, 只要符合Services規(guī)范的程序就可以接入到Router并進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)的路由.
Factory模式和Composite模式
XMLRouter在實(shí)際的設(shè)計(jì)中將采用Factory模式產(chǎn)生,Router由RouterFactory生產(chǎn), 在投入使用時(shí)將放置于隊(duì)列中,傳遞數(shù)據(jù)和接收數(shù)據(jù)以及返回?cái)?shù)據(jù)都從隊(duì)列中取相應(yīng)的Router來(lái)調(diào)用,應(yīng)用了Composite的模式.
四.XML配置文件
XML文件對(duì)于Router之中的使用分為兩個(gè)部分, 第一個(gè)是Router的配置,如:
| 以下是引用片段: <?xml version="1.0" ?> <services> <!-- database Service --> <service name="database" type="database" class="com.web.service.DBService"> <connector driver="com.microsoft.jdbc.sqlserver.SQLServerDriver" url="jdbc:microsoft:sqlserver://192.168.0.179:1433" user="test" passwd="test" /> </service> <!-- Web Service--> <service name="web" type="web" class="com.web.service.WebService" > <connector /> </service> …… </services> |
這是Router的配置文件, service節(jié)點(diǎn)代表需要接入的渠道, service節(jié)點(diǎn)包含connector子節(jié)點(diǎn), 子節(jié)點(diǎn)的配置根據(jù)type來(lái)區(qū)分, 如果是database則包含url, user, passwd,driver等屬性, 如果是socket則包含 port, maxthread等屬性, 屬性值可以根據(jù)自己的定義來(lái)配置.
另一種XML文件則是XML交易數(shù)據(jù)文件,用于在所有的services中傳遞數(shù)據(jù),每個(gè)Services自己包涵一個(gè)相應(yīng)的XML文件,比如webtrans.xml格式如下:
| 以下是引用片段: <?xml version="1.0" ?> <transaction> <trans name="addDoc" service="database" method="insert"> <property name="createtime" type="timestamp"/> <property name="creatorid" type="long"/> <property name="doctypeid" type="int"/> <property name="docstatusid" type="int"/> </trans> </transaction> |
相應(yīng)的dbtrans.xml格式如下
| 以下是引用片段: <trans name="addDoc" table="TDOC_DOCS" method="insert"> <primarykey name="docid" /> <set> <property name="createtime" type="timestamp"/> <property name="creatorid" type="long"/> <property name="doctypeid" type="int"/> <property name="docstatusid" type="int"/> </set> </trans> |
其余XML則可按這樣的規(guī)則來(lái)定制
五.技術(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn)
RouterFactory
| 以下是引用片段: package com.web.router; import com.web.platform.Exception.RouterException; import java.util.java/util/Hashtable.java.html" target="_blank">Hashtable; |
| 以下是引用片段: /** * Router產(chǎn)生和清除的類 */ public class RouterFactory { /** * Router存儲(chǔ)的樹(shù)front */ private static java/util/Hashtable.java.html" target="_blank">Hashtable QueuePairFront = null; /** * Router存儲(chǔ)的樹(shù)back */ private static java/util/Hashtable.java.html" target="_blank">Hashtable QueuePairBack = null; /** * Router存儲(chǔ)的樹(shù) */ private static java/util/Hashtable.java.html" target="_blank">Hashtable QueueRouter = null; /** * 返回的XMLRouter */ public static XMLRouter instance = null; /** * Router的定義 */ public static RouterDefine routerdefine = null; /** * Router的ID號(hào) */ public static long routeIndex = 0; /** * @roseuid 3F169C21027C */ public RouterFactory() { } /** * 初始化Hashtable和Vector */ public static void initFactory() throws java/lang/Exception.java.html" target="_blank">Exception { QueuePairFront = new java/util/Hashtable.java.html" target="_blank">Hashtable(); QueuePairBack = new java/util/Hashtable.java.html" target="_blank">Hashtable(); QueueRouter = new java/util/Hashtable.java.html" target="_blank">Hashtable(); initRouteDefine(); } /** * 初始化Route的設(shè)置 * */ private static void initRouteDefine() throws java/lang/Exception.java.html" target="_blank">Exception { if( routerdefine == null ) routerdefine = new RouterDefine(); routerdefine.loadRouterDef(); } /** * 返回實(shí)例 * @return com.web.router.XMLRouter */ public static XMLRouter getInstance(long index) throws RouterException { return (XMLRouter)QueueRouter.get(new java/lang/Long.java.html" target="_blank">Long(index)); } /** * 產(chǎn)生一個(gè)XMLRouter的實(shí)例 * @return com.web.router.XMLRouter * @roseuid 3F1618A103BC */ public static XMLRouter popInstance() throws RouterException { routeIndex ; instance = new XMLRouter(routeIndex); setDefine( instance ); QueueRouter.put(new java/lang/Long.java.html" target="_blank">Long(routeIndex), instance); return instance; } /** * 清空Hashtable,Vector等 * @roseuid 3F1618B203C1 */ private static void freeResource() throws java/lang/Exception.java.html" target="_blank">Exception { QueuePairFront.clear(); QueuePairBack.clear(); QueueRouter.clear(); QueuePairFront = QueuePairBack = QueueRouter = null; } /** * 清除實(shí)例 * @param instanceID * @throws Exception */ public static void removeInstance(XMLRouter instance) throws java/lang/Exception.java.html" target="_blank">Exception { instance.clear(); QueueRouter.remove( new java/lang/Long.java.html" target="_blank">Long(instance.getIndex() ) ) ; } /** * Method isNull. * @return boolean */ public static boolean isNull() { …… return false; } } |
XMLRouter
| 以下是引用片段: package com.web.router; import com.web.platform.Exception.RouterException; import com.web.common.*; import java.util.*; import java.lang.reflect.java/lang/reflect/Method.java.html" target="_blank">Method; import java.lang.reflect.java/lang/reflect/Constructor.java.html" target="_blank">Constructor; /** * @author keli * @version 0.0.1 * 平臺(tái)的關(guān)鍵,路由的類,每個(gè)Router將從RouterFactory里讀取 * Router存儲(chǔ)的樹(shù)front,和back,routeIndex,目的是為了能在路由 * 之后可以清除申請(qǐng)的對(duì)象。 * Router可以實(shí)現(xiàn)同步和異步的功能. */ public class XMLRouter { /** * Router存儲(chǔ)的樹(shù)front */ private static java/util/Hashtable.java.html" target="_blank">Hashtable QueuePairFront = null; /** * Router存儲(chǔ)的樹(shù)back */ private static java/util/Hashtable.java.html" target="_blank">Hashtable QueuePairBack = null; /** * 本router的index號(hào)碼 */ private long routeIndex = 0; /** * router的設(shè)置 */ private RouterDefine define = null; /** * 用于判斷是路由的起回點(diǎn) */ private java/lang/String.java.html" target="_blank">String action = ""; /** *此變量只是用于在routeto方法中申請(qǐng)新的class */ private java/lang/String.java.html" target="_blank">String classname = ""; /** */ public XMLRouter(long index) { routeIndex = index; } /** * 路由 * @throws Exception * @roseuid 3F1616BD0186 */ public void routing(Env env) throws RouterException, java/lang/Exception.java.html" target="_blank">Exception { /*如果為起點(diǎn)*/ if( action.equalsIgnoreCase( RouterConstant.CFG_FUNC_ROUTETO ) ) { …… } /*如果為返回點(diǎn)*/ else if( action.equalsIgnoreCase( RouterConstant.CFG_FUNC_ROUTEBACK ) ) { …… } /*否則為錯(cuò)誤*/ else throw new RouterException("Set Router action error."); } /** * 讀取本Router的id號(hào). * @return long */ public long getIndex() { return routeIndex; } /** * 清除所有對(duì)象. * @throws RouterException */ public void clear() throws RouterException { QueuePairFront.remove(new java/lang/Long.java.html" target="_blank">Long(routeIndex)); QueuePairBack.remove(new java/lang/Long.java.html" target="_blank">Long(routeIndex)); /*系統(tǒng)回收*/ java/lang/System.java.html" target="_blank">System.runFinalization(); } /** * 設(shè)置本Router的設(shè)置. * @param def * @throws RouterException */ public void setDefine(RouterDefine def) throws RouterException { define = def; } /** * 設(shè)置action的值 * @param actionName * @throws RouterException */ public void setAction( java/lang/String.java.html" target="_blank">String actionName ) { action = actionName; } } |
Service類
| 以下是引用片段: package com.web.common; import com.web.platform.Exception.RouterException; /** * Service的父類,abstract */ public abstract class RouteService { /** */ public RouteService() { } /** * routeTo方法,是交易的起點(diǎn)。 * @param env * @throws RouterException */ public abstract void routeto(Env env) throws RouterException; /** * routeBack,交易的結(jié)束點(diǎn), * @param env * @throws RouterException */ public abstract void routeback(Env env) throws RouterException; /** * routeaccept方法,是交易的接收點(diǎn),也是routeto的接收函數(shù), * routeaccept為被動(dòng)交易對(duì)象的主要處理函數(shù) * @param env * @throws RouterException */ public abstract void routeaccept(Env env) throws RouterException; /** * routing方法,是Service對(duì)外的接口函數(shù) * @throws RouterException */ public abstract void routing() throws RouterException; |
接下來(lái)則需要實(shí)現(xiàn)所有的Services的類了,這里就不做介紹了.
六.說(shuō)明
這個(gè)Router到目前為止只能實(shí)現(xiàn)同步的交易, 暫時(shí)不支持異步的交易,但是由于對(duì)Router使用了Composite的模式設(shè)計(jì)的,實(shí)現(xiàn)異步交易也是可以擴(kuò)展的,這里不做詳細(xì)分析.
分享:解析XML數(shù)據(jù)查詢技術(shù)已經(jīng)成為現(xiàn)今的研究熱點(diǎn)XML(可擴(kuò)展標(biāo)記語(yǔ)言)已成為Web應(yīng)用中數(shù)據(jù)表示和數(shù)據(jù)交換的標(biāo)準(zhǔn),隨著Internet的快速發(fā)展,尤其是電子商務(wù),Web服務(wù)等應(yīng)用的廣泛使用,XML類型的數(shù)據(jù)成為當(dāng)前主流的數(shù)據(jù)形式。因此XML數(shù)據(jù)的管理技術(shù)
- xml創(chuàng)建節(jié)點(diǎn)(根節(jié)點(diǎn)、子節(jié)點(diǎn))
- WML開(kāi)發(fā)教程之 WAP網(wǎng)站服務(wù)器配置方法
- WMLScript的語(yǔ)法基礎(chǔ)
- 收集的WML Script標(biāo)準(zhǔn)函數(shù)庫(kù)
- WML教程之文本框控件Input
- 無(wú)線標(biāo)記語(yǔ)言(WML)基礎(chǔ)之WMLScript 基礎(chǔ)
- xml文件的結(jié)構(gòu)解讀
- 關(guān)于XSL - XSL教程
- 選擇模式 - XSL教程 - 2
- XPath入門 - XSL教程 - 3
- 匹配模式 - XSL教程 - 4
- 測(cè)試模式 - XSL教程 - 5
- 相關(guān)鏈接:
- 教程說(shuō)明:
Xml教程-怎樣使用XML實(shí)現(xiàn)多渠道接入網(wǎng)站的構(gòu)架
 。
。